In the digital age of today, your information is the most valuable asset, both for yourself and for those looking to steal it. One of the most trusted ways of protecting this asset is the concept of encryption; to use a traditional, physical lock or a physical keypad as an analogy, it is the practice of putting your information into a vault, and locking it with a key or a code that only you (the owner) have access to, and thus preventing potential bad actors from accessing it. The goal is to encrypt data in a manner that it remains confidential unless intentionally shared. The digital equivalent of this practice is something you may want to consider repeating for your external hard disk, which we will show you how to do in this guide.
What is External Hard Drive Encryption?
To answer the question of what external hard drive encryption is, we first have to look at what encryption is, before delving deeper into the encryption process itself for your external hard drive.
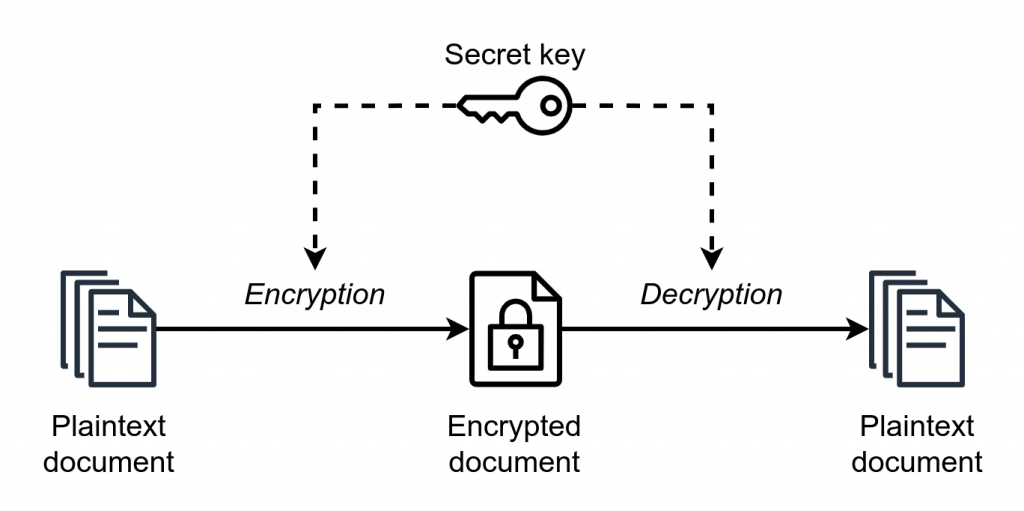
Encryption is not only about transforming data but ensuring data security through this transformation. Encryption is, simply put, the process of taking human-readable information, also known as plaintext, and converting it into something known as ciphertext. Ciphertext, as the name would suggest, is text that has been modified by a cipher, which is an algorithm that defines how the process of turning plaintext to ciphertext works. While plaintext can be read by anybody, ciphertext can be read only by those possessing the keys (decryption keys) for reversing the encryption procedure.
For Linux Operating System users, an important aspect of encryption is the Linux Unified Key Setup (LUKS), which provides a standard for disk encryption. Modern ciphers can be divided into two distinct categories:
- Symmetric-key algorithms (i.e, private-key cryptography)
- Asymmetric-key algorithms (i.e, public-key cryptography)
Public-key cryptography is most commonly used for transmitting data between two parties (i.e, when it is in transit), and works using both a private key, held by the recipient of the message and a public key (of the recipient), used by the sender to encrypt the message. Meanwhile, private-key cryptography is more commonly used when the data is at rest, or simply put, stored on a device that only one intending party needs to have access to, and uses only a singular key (same key) for the entire encryption process.
When encrypting data on your external hard drive, USB drive, and other storage devices, private-key cryptography is most commonly used, since data is not being transmitted from one party to another, and therefore no mechanism is required for the encryption of data using the recipient’s public key.
So, therefore, in principle, external hard drive encryption is the process of converting the information on your external drive from something readable by everybody, into only something readable by you, who possesses the key.
To encrypt an external hard drive, one must understand the encryption method suitable for their operating system and hardware. We recommend you perform the act of encrypting external hard drives and important data, especially if you are looking to password protect and seal your data from potential data breaches, maintain data integrity, prevent bad actors from accessing your sensitive information, along with Personally Identifiable Information (PII), or are concerned that the data protection regulations in your area don’t aptly protect your data stored on them.
Most Common Types of Disk Encryption
Before encrypting your external hard disk, USB drive, or any other external storage drive, you should be aware of the most common types of disk encryption and ways to encrypt an external hard drive, or any other file system, for which there are many ways. This will help you determine the best one for your use case.
The following types of disk encryption are most commonly used in the process of encrypting an external hard drive:
- Full Disk Encryption:
As the name would suggest, full drive encryption performs the process of disk encryption on your entire external hard drive, and its FS. This method ensures that every encrypted file on the drive is secured, providing an extensive layer of data security. Most modern operating systems, including macOS and your Windows computer, allow you to easily encrypt your hard drive, without having to resort to using any third party versions of encryption software, or disk utility.
- Self-Encrypting Drive:
Self Encrypting Drives, also known as SEDs, are storage devices that allow users to protect data using encryption in real-time, which is performed using hardware based encryption on the drive itself. An encrypted drive of this kind provides robust protection against unauthorized access. All the data on your external hard drive, usb flash drive, memory cards, or any other external storage devices are encrypted, even when changes are made to the data stored on them. It is an example of a storage device performing hardware based encryption.
- Filesystem-level Encryption:
This type of encryption is used for encrypting only singular files on your external storage device, or file system of choice, and is one of the most common encryption methods. It allows for an encrypted volume to be created within the drive where specific files can be securely stored. The user can choose the file which they are going to encrypt, and the encryption task is simple to perform using third party encryption software and allows for the user to password protect their files using different passwords, and keeping them in a secure location within themselves.
- Cloud Encryption
This type of encryption focuses on cloud storage, and the data and files contained within. A wide variety of cloud storage providers allow their users to store data and simultaneously protect this data using built in tools from data breaches which those cloud storage providers may in the worst-case scenario be affected by.
In the nowadays digital age, the encryption system used for cloud storage is crucial to protect against data breach incidents.
The Encryption Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The question of how to encrypt an external hard drive depends in some aspects on the question of whether the process is performed using a Windows computer or a computer running macOS. Regardless, the actual process remains widely the same, with both Windows operating systems, and macOS being shipped with built-in software, allowing you to easily encrypt an external hard drive, and password protect it, without the need for any third party software.
On Windows Computers
On Windows PCs, the practice of encrypting your external drive, USB flash drives, or any other external storage device, can be very easily performed using a built-in tool called BitLocker, as visualized by the steps below:
- Open File Explorer (Windows Explorer).
- In the address bar, type the following: Control Panel\All Control Panel Items\BitLocker Drive Encryption. This will take you directly to the BitLocker Drive Encryption page in the Control Panel.
- On the BitLocker page, choose the external hard drive that you want to password protect and encrypt. External hard disks, along with USB drives are usually listed under “Removable Data Drives”.
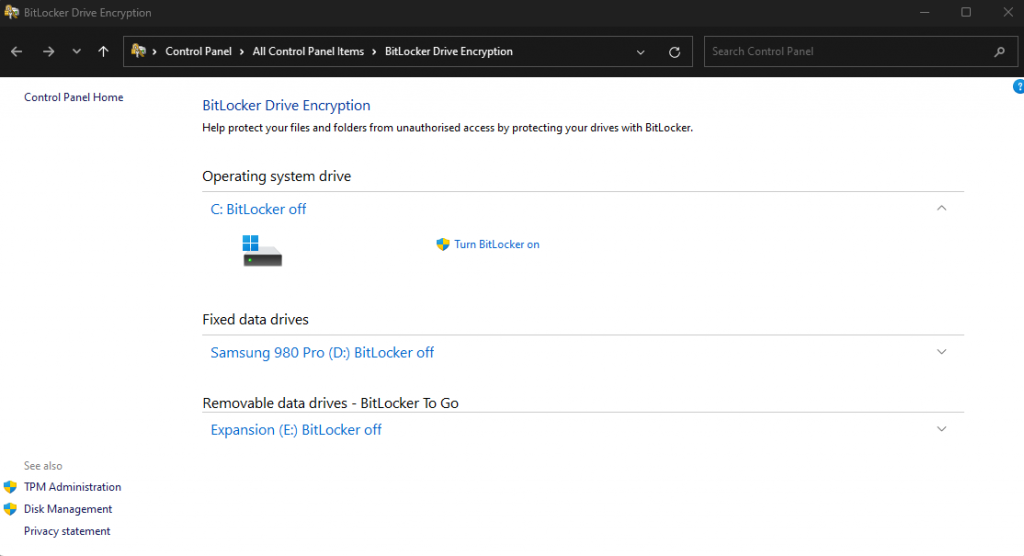
- Click “Turn BitLocker on”.
- You will be asked to choose between a password, a smart card, or both. Choose your password, or enter your smart card, along with its PIN. Click on “Next”.
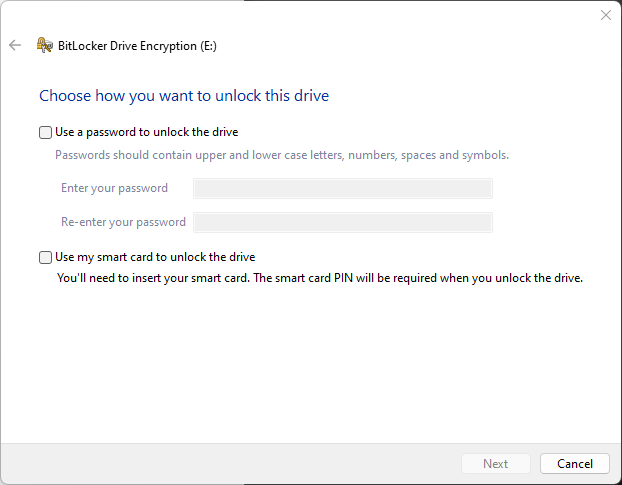
- Next, click ‘Encrypt disk’ to begin the encryption of the selected drive.
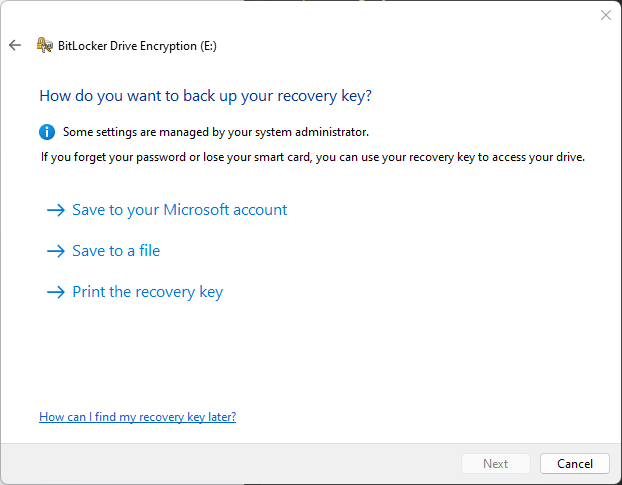
- Next, you will be asked to choose how your recovery key will be backed up. Choose one of the three options and click “Next”. This key will allow you to access your encrypted external hard drive, in case you forget the correct password; no password hint is provided as an option.
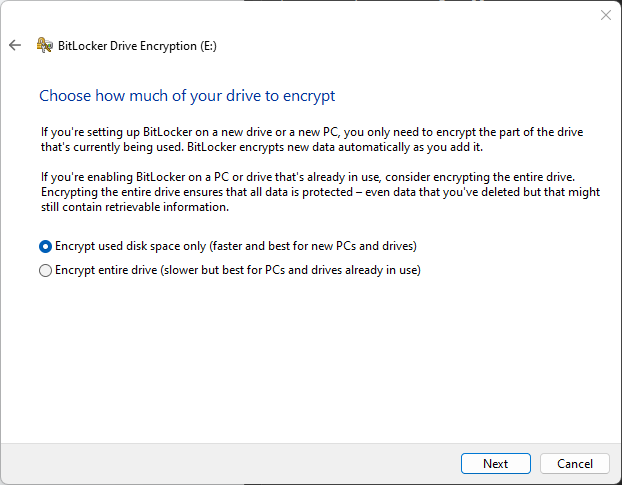
- Choose the portion of the external hard drive that you want to encrypt; the options being the encryption of all disk space that is currently used on the external drive or encrypting the entire disk.
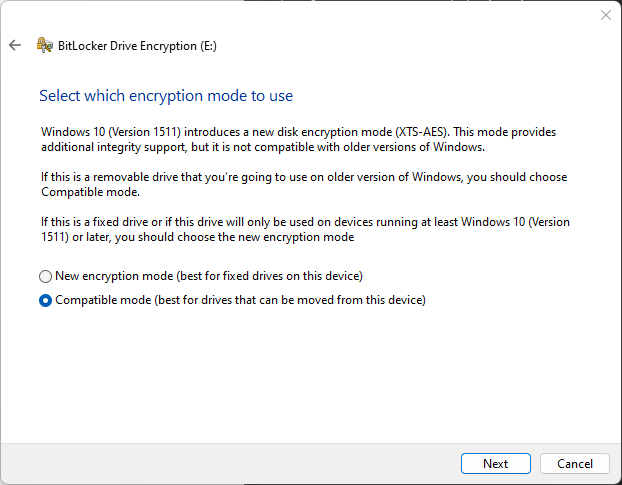
- Choose the encryption mode. The options are between the latest encryption mode introduced in Windows 10 (Version 1511), which uses the XTS-AES cipher, or using compatibility mode, in case you will be using the external hard drive on older versions of Windows.
- In the final step, click “Start encrypting”, and your external hard drive will be with encrypted data by BitLocker.
On macOS
On Mac-based computers, the process of external hard drive encryption can similarly be accomplished using a built-in tool – in this case, the Disk Utility.
It is essential for Mac users to select 'Mac OS Extended (Journaled)' as the format if the drive will be used predominantly with macOS.
Note: This should only be performed on empty volumes. In case your external hard drive contains any files, move them to another location before attempting to encrypt it.
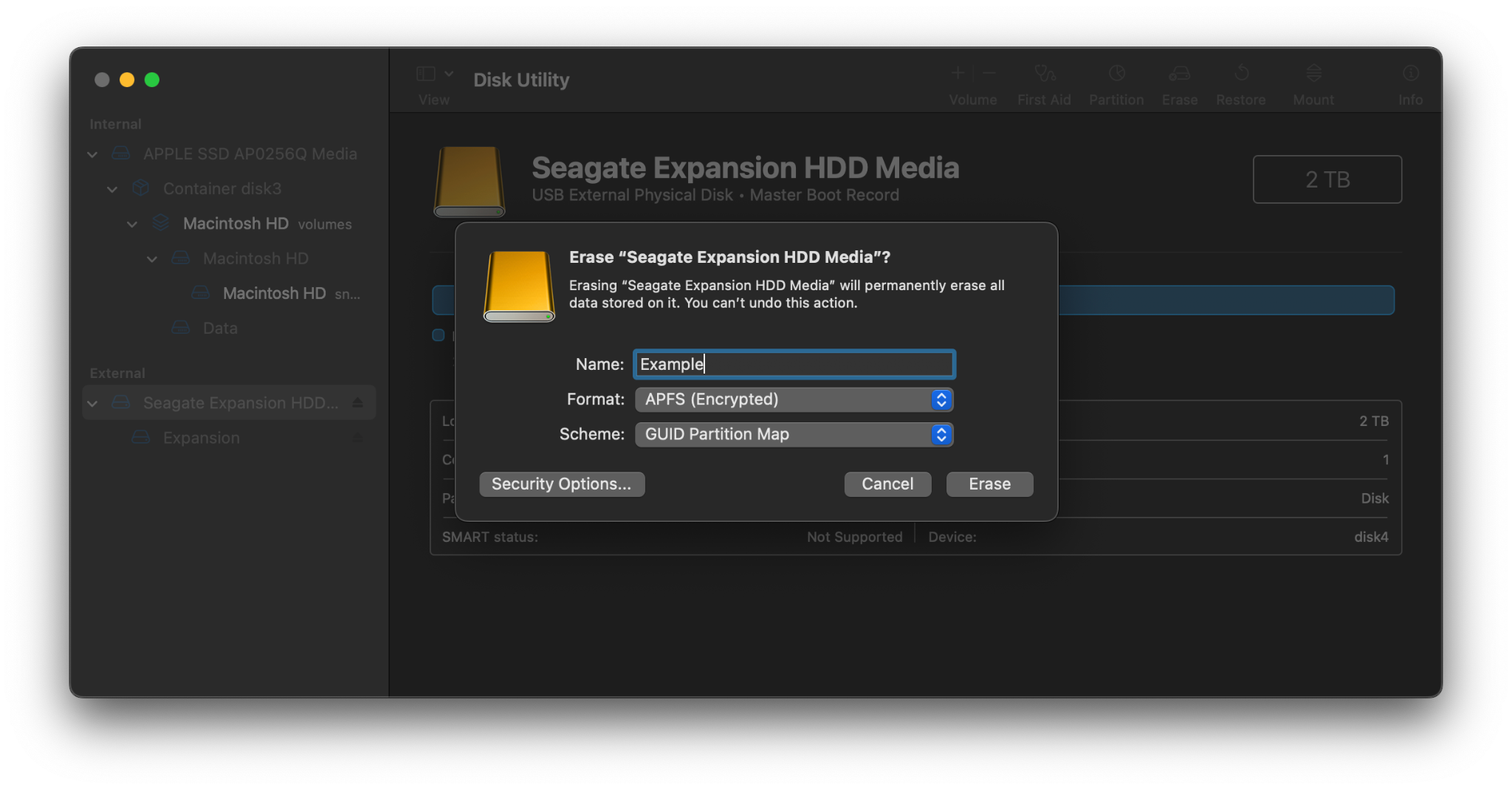
- Open Disk Utility on your Mac.
- From the sidebar, select the external hard drive you wish to encrypt.
- In the toolbar, click the erase button.
- In the new window, provide the volume with a new name.

- Choose APFS (Encrypted) as your “Format” option.
- A new window will open. Enter your password, and optionally, a password hint.
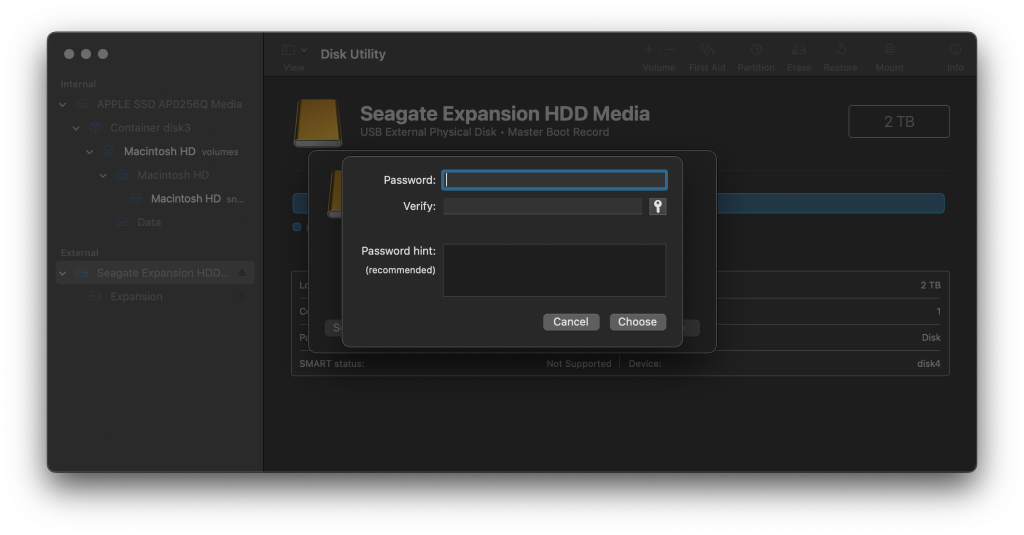
- For your Scheme, select “GUID Partition Map”.
- Click the “erase” button. This will completely erase any data. The new, empty volume will be encrypted.
Using a portable drive with sensitive information necessitates extra precautions. Encrypting it ensures data security even if it is lost or stolen.
Recovery Key: In case you forget your password
Whenever you password protect and encrypt your external hard drive or other storage device, you should remember to note down the provided recovery key in preparation for the instance you forget your password.
Usually, it comes in the form of a file you can download, or even the option of saving it to your account (such as in the case of BitLocker). This key should always be stored in a secure location and one where you are sure you will always be able to find it if the worst comes to be.
Setting a password reminder is also an alternative you can choose if presented as an option.
Advantages and Disadvantages of External Hard Drive Encryption
We recommend you perform the act of encrypting external hard drives and important data, especially if you are looking to password protect and seal your data from potential data breaches, maintain data integrity, prevent bad actors from accessing your sensitive information, along with Personally Identifiable Information (PII), or are concerned that the data protection regulations in your area don’t aptly protect your data stored on them. And knowing how to encrypt an external drive puts you one step ahead. Simply put, the largest advantage of encryption is the protection of your valuable information.
The largest disadvantages of external hard drive encryption are considerations such as the humane mistake of potentially forgetting your password and rendering your data unavailable. Additionally, encryption is only as good as your encryption key, i.e., your password, so be sure to select a complex one.
In the longer term future, one has to also consider the possibility of quantum computing, and its ability to break even the strongest of our current, classical cryptographic algorithms, rendering them practically useless.